Melatonin, 5-HTP, and Ashwagandha
Melatonin is a hormone made by your brain that helps regulate your body’s internal clock. Your levels of melatonin increase at night and decrease during the day.
Melatonin synthesis begins with the amino acid L-tryptophan. L-tryptophan is converted into 5-HTP then 5-HTP is converted to serotonin, which is then metabolized further to create melatonin. Melatonin does not function like the neurotransmitter serotonin; instead, it triggers the sleep cycle by interacting with its own receptors in the brain.
Melatonin can interact with antidepressants, antipsychotics, benzodiazepines, high blood pressure medications, blood thinners, NSAIDs, steroids and tamoxifen, a chemotherapy drug used in the treatment of breast cancer. Melatonin also interacts with caffeine, tobacco and alcohol, all of which lower the levels of melatonin in the body.
Serotonin, also called 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT), is one of the most important brain chemicals, or neurotransmitters, for regulating the sleep/wake cycle.
5-HTP is sometimes used as sleep aids, but it is serotonin that has the antidepressant, mood elevating and anti-anxiety effects that make sleep possible. Very little 5-HTP comes from the foods you eat. Instead, your body produces 5-HTP from the tryptophan found in protein-rich foods like eggs, meat, fish and dairy products.
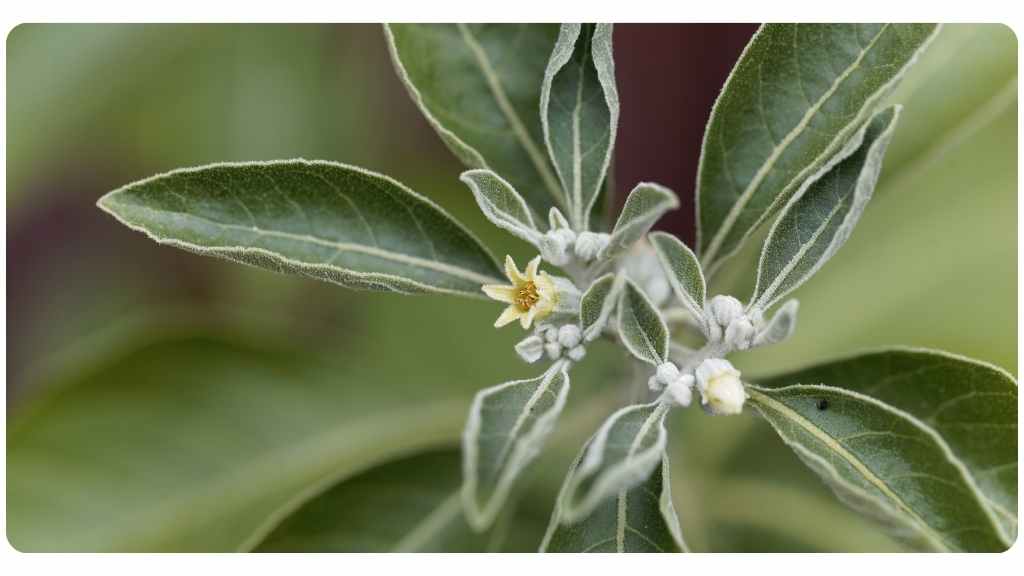
Recent clinical research has shown ashwagandha to play a role in treating stress, anxiety, depression and insomnia as well as cognitive enhancing, neuroprotective, antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and other effects. Ashwagandha also has adaptogenic properties, meaning that it strengthens the immune system and helps the body counteract stress.
Ashwagandha is generally well tolerated, and regarded as safe when taken within the therapeutic dosage range. A caution, it is best avoided by those with known sensitivities to members of the solanaceaea family. Finally, being a mild central nervous system depressant, ashwagandha should not be taken with alcohol, sedatives or anxiolytics as it can potentiate the effects of these.